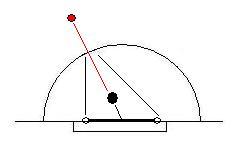
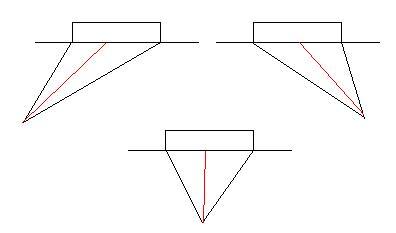
To help you gage where you are when you cialis 5mg move on or off the post, you can use your hands effectively to help you out: the further you are away from the post, the further you have to reach back to find out where you are in relation to the goal and your angles. Once you’ve found the goal post, you should be able to step backwards successfully onto the post, ready to cut off a possible shot. This allows you to reset your angles and set your positioning for a potential save or block: aware of where you are in relation to the amount of net space you cover (by standing over or away from the post) according to the expected shot; ready to move off, into a save off and outside the post, if the shooter decides to target that area instead.
Knowing your angles is essential to finding your whereabouts in order to move around the posts in order to make saves. If you happen to watch GB’s current no. 1, Alistair MacGregor of Loughborough Students, you’ll notice this is a technique he has perfected down to a tee.
‘Tapping’ the posts
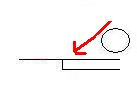
When moving off your glove side goal post to step out into the play, you can reach back and out with your glove arm; tapping the post with your glove to check your positioning in relation to the goal. Just like soccer goalkeepers that ‘punch’ the post with the side of their bunched up fist, or tapping with their fingers, you can tap the inside post with top of your glove, or push against it with your palm. You can basically ‘feel’ your way around to work out where you should be standing. This way, you are able to find where you are in relation to the post (and goal in general) and then reset your angles accordingly to deal with the action around you.
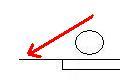
For movement onto and off your right post, you can use a similar technique to find the goal post with your stick; swinging it round to tap against the post to check the line of angle. Like ice hockey goalies who regularly tap their posts to check their bearings, you can use your stick actively; pushing out to tap the post. Check the noise made; the louder, the better. Theoretically, the louder the sound is, the closer the post is (helpful if you are too busy focusing on the play to look at the post itself), whereas the quieter it is, the further away the post is. The distance you have to reach out with the stick will also tell you how far you are from the post – if you have to extend the stick to reach it, then you are too far away from it.